As renewable energy technologies have grown, GIS has become an essential ally in identifying ideal locations for these inherently geographic solutions for energy production. Spatial analysis can reveal prime areas for renewable energy production by calculating the energy potential of a given location based on the geographic and cultural landscapes.
Applying GIS for wind energy enables a streamlined site selection process, and provides the ability to add all influencing factors into a single map. For wind farms, primary factors to consider include wind speed, land use, population density, distance to road, slope, and distance to transmission lines.
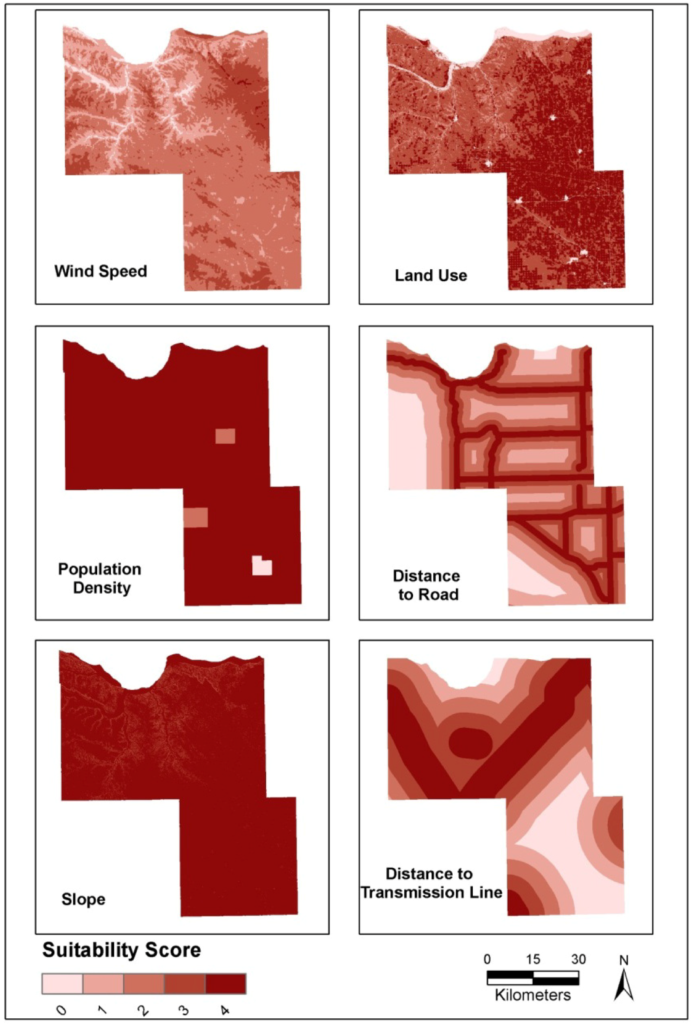
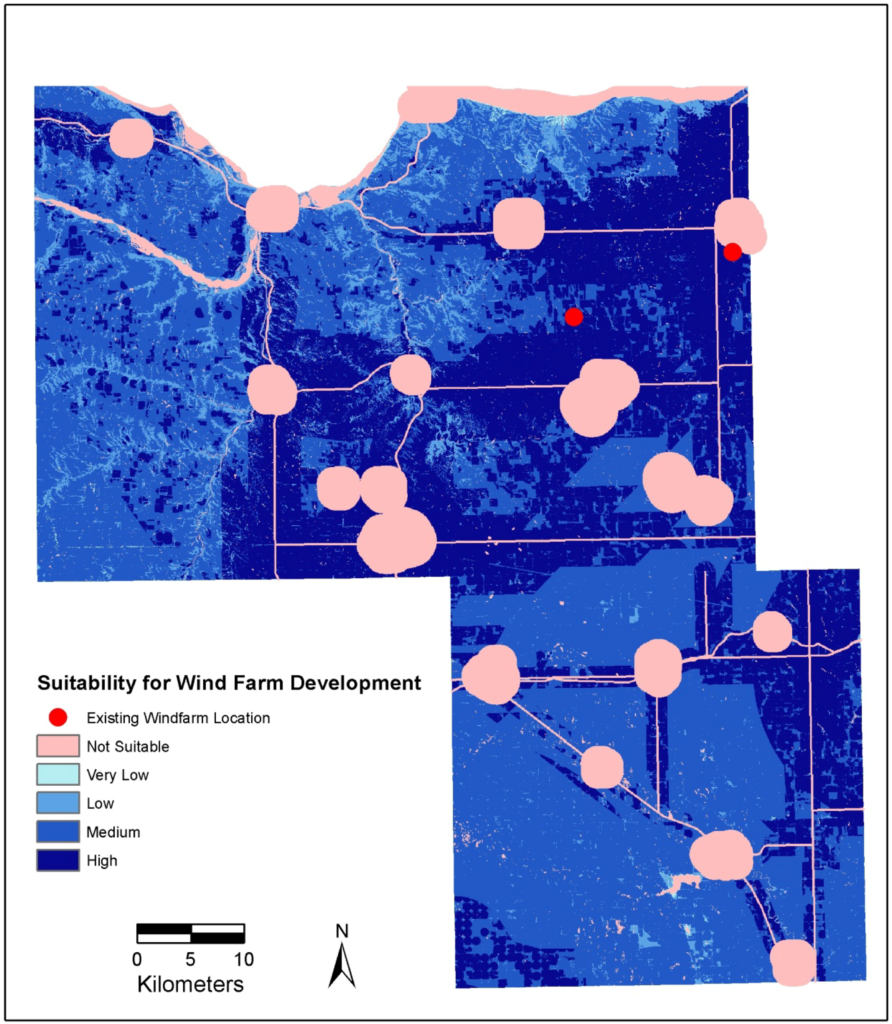
Spatial analysis helps to pinpoint ideal site locations. Buffer zones are created around given features to set off-limits locations for wind turbines. By combining data layers for each limitation with the map area, available sites are revealed through the cracks. The next step is to overlay the resource potential of a given area.
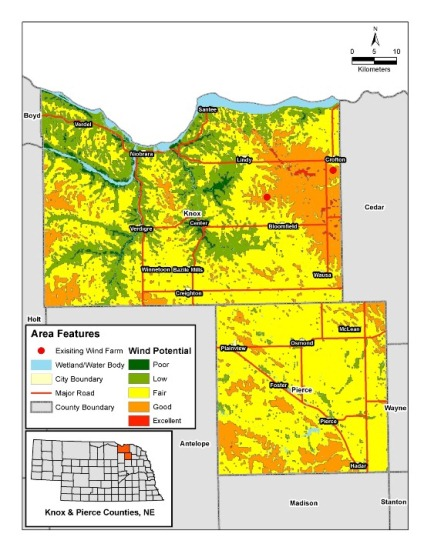
In the development of a wind farm, everything begins with selecting the ideal location. The proximity of transmission lines is a key factor when determining a suitable site. Although, with ideal conditions and constant heavy wind, decision-makers may be motivated to build a new transmission line to reach an ideal area.
But heavy winds and the location of transmission lines aren’t the only factors taken into consideration during the site selection phase. There are plenty of environmental constraints to consider, such as migratory bird flight paths and migration routes. GIS is a powerful tool that allows for all these factors to be depicted at once in a single suitability map.
“Almost all the wind power facility layouts can be done with GIS, with maybe one or two visits to the field. Now we can stock the GIS with U.S. Geological Survey maps, property lines, aerial photography, and detailed topographic data to see how the buildable area matches up with the wind data.” – Tyler Hoffbuhr, GIS analyst and manager with Iberdrola Renewables.
Hands-on Training Exercise
Learn how to create your own suitability analysis to determine the best location for a new wind farm in Colorado. This free 1-hour lesson from Esri will teach you how to conduct a site suitability analysis, route to prospective sites, and create a web app to showcase your findings.
Learn more about wind energy potential
- Browse the Global Wind Atlas
- Reveal India’s Wind Energy Information
- Read more on Wildlife and Wind Energy
- Discover a variety of wind maps from NREL
Get Support
Whether for renewable energy site selection, or simply to gain a better understanding of your data, spatial analysis enables informed decisions, and leads to more successful results. Reach out to our industry experts to learn how you can leverage the power of GIS and spatial analysis for your business objectives.



